Table of Contents
im starting a new page as the old one is a bit outdated.
TTgo
playing with the (in)(not)famous TTGO T-Journal
goal: creating a tamper-proof system for scientific data by linking them and their metadata to an unfalsifiable signature in the blockchain.
more informations on this research page: BIDI2021
Receiving the HTTP Stream (multipart/x-mixed-replace | Content-Type: image/jpeg ):
vlc http://172.20.10.8 #(IP of the board)
Saving a Picture with FFMPEG:
ffmpeg -y -i http://172.20.10.8 -ss 0 -vframes 1 -vcodec mjpeg -f image2 tomato.jpg
Saving + Adding a SHA256 MetaData:
ffmpeg -y -i http://172.20.10.8 -ss 0 -vframes 1 -vcodec mjpeg -f image2 tomato.jpg && exiv2 -M"set Exif.Photo.UserComment F902F4FD763A551D5387C224D34A9C9A0B383850386EC1509EB232A49DE5D5F9" tomato.jpg
Reading the MetaData:
exiv2 tomato.jpg
File name: tomato.jpg File size: 8974 Bytes MIME type: image/jpeg Image size: 800x600 Exif comment: F902F4FD763A551D5387C224D34A9C9A0B383850386EC1509EB232A49DE5D5F9
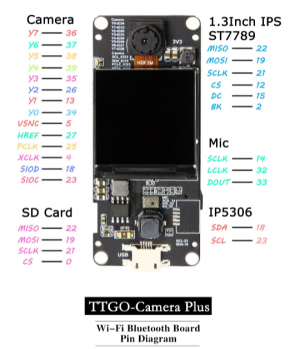
TTgo CAMERA PLUS bigiot
T-Camera Plus Esp32-Dowdq6 8Mb Spram Camera Module Ov2640 1.3 Inch Display Rear Camera(Fish-Eye Rear Camera)
TTGO Camera Plus Standalone Camera firmware
https://www.instructables.com/Arduino-Selfie-Camera/
https://github.com/moononournation/arduino-selfie-camera
Install Arduino IDE https://linuxhint.com/install_arduino_ide_debian_10/
Install ESP32 in the Board manager and choose “ESP32 Dev”“ or install manually thanks to (Debian) https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/blob/master/docs/arduino-ide/debian_ubuntu.md
I had this error:
File "/home/me/Arduino/hardware/espressif/esp32/tools/esptool/esptool.py", line 38, in <module> import serial ImportError: No module named serial
I have fix this issue with following steps:
Download the pyserial package from: https://pypi.org/project/pyserial/#files
tar zxvf pyserial-3.0.tar.gz
cd pyserial
sudo python setup.py install
Open the .ino file after downloading code from https://github.com/anonette/NonFungibleScience/tree/main/CAM
Compile and Transfer
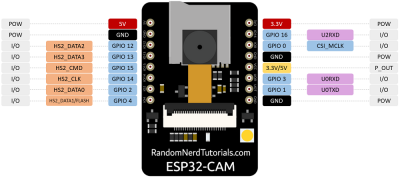
AI-thinker
using the esp-cam32 AI-thinker module.
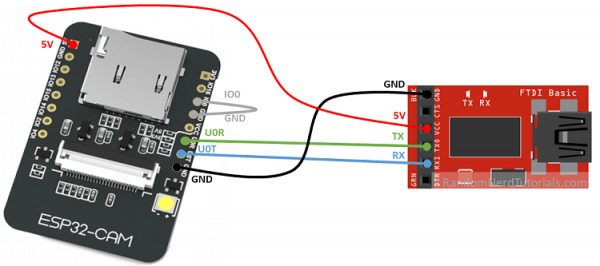
viarandomNerd
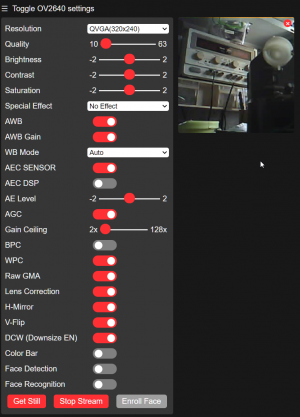
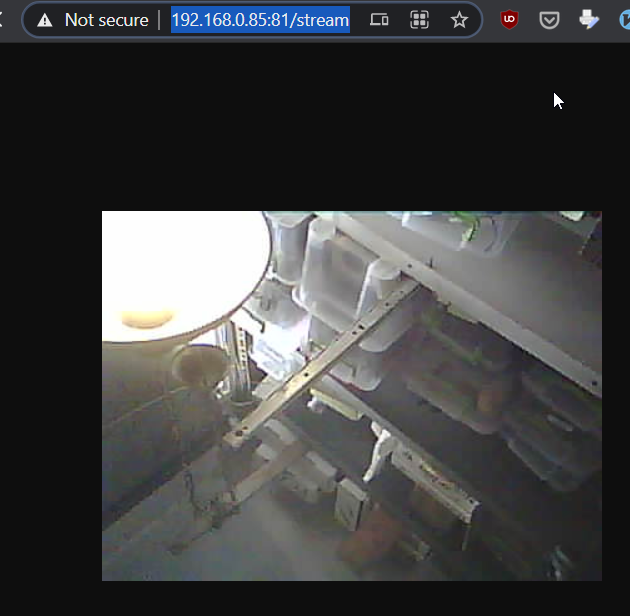
output of CameraWebServer
gstreamer to file
gst-launch-1.0 souphttpsrc location=http://192.168.0.85:81/stream do-timestamp=true ! multipartdemux ! image/jpeg,width=640,height=480 ! matroskamux ! filesink location=mjpeg.mkvD
The above pipeline reads a motion JPEG stream from an IP camera using the HTTP protocol, encoded as mime/multipart image/jpeg parts, and writes a Matroska motion JPEG file. The width and height properties are set in the caps to provide the Matroska multiplexer with the information to set this in the header. Timestamps are set on the buffers as they arrive from the camera. These are used by the mime/multipart demultiplexer to emit timestamps on the JPEG-encoded video frame buffers. This allows the Matroska multiplexer to timestamp the frames in the resulting file.
python/ffmpeg/opencv
install conda env
sudo apt install libgl1-mesa-glx libegl1-mesa libxrandr2 libxrandr2 libxss1 libxcursor1 libxcomposite1 libasound2 libxi6 libxtst6 wget -P /tmp https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2020.02-Linux-x86_64.sh bash /tmp/https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2020.02-Linux-x86_64.sh conda create --name opencv -c conda-forge opencv conda activate opencv pip install opencv-contrib-python python testSource.py ['FFMPEG', 'GSTREAMER', 'INTEL_MFX', 'MSMF', 'V4L2', 'CV_IMAGES', 'CV_MJPEG', 'UEYE'] ['GSTREAMER', 'MSMF', 'V4L2', 'UEYE']
invest time in
https://github.com/geeksville/Micro-RTSP - library which can be used to serve up RTSP streams from resource constrained MCUs